
Supply Chain Attacks: A Growing Threat to Your Business
- By ThreatMatrix
Introduction
In today’s interconnected digital world, businesses rely on complex supply chains to deliver goods and services. While these supply chains offer numerous benefits, they also present significant cybersecurity risks. Supply chain attacks, where malicious actors target vulnerabilities in a company’s supply chain to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data or disrupt operations, have become increasingly prevalent.
Understanding Supply Chain Attacks
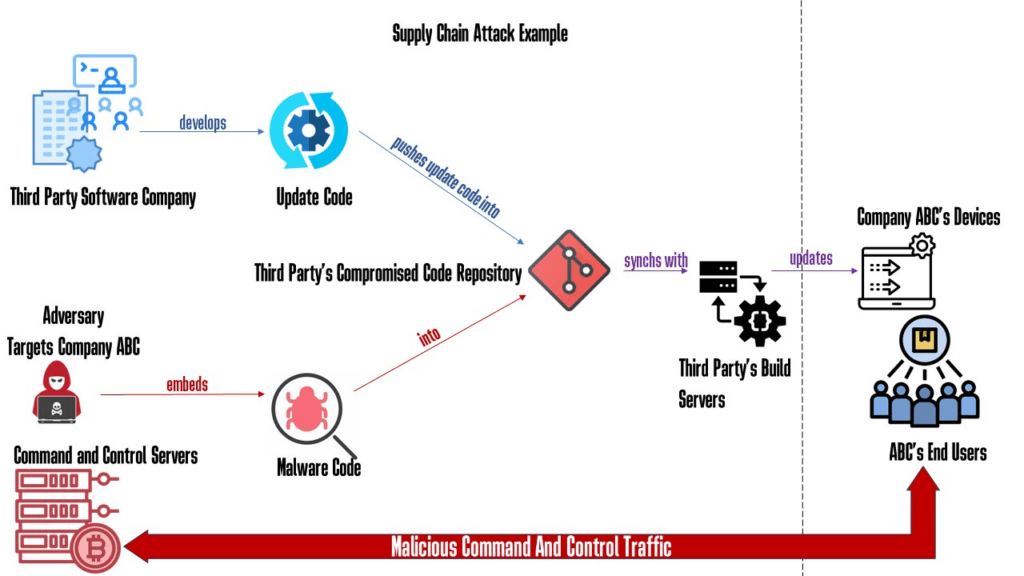
A vendor attack involves compromising a third-party vendor or supplier to gain access to a target organization. Attackers may exploit vulnerabilities in software, hardware, or even human error to infiltrate the supply chain. Once inside, they can steal data, disrupt operations, or deploy ransomware.
Common Tactics Used in Supply Chain Attacks
- Software Supply Chain Attacks: Malicious actors target software development tools, code repositories, or software updates to introduce malicious code.
- Hardware Supply Chain Attacks: Attackers may compromise hardware components or manufacturing processes to insert malicious hardware.
- Third-Party Vendor Attacks: Targeting vulnerabilities in third-party vendors, such as cloud service providers or IT service providers.
- Phishing and Social Engineering: Manipulating employees to reveal sensitive information or download malicious software.
How to Protect Your Business from Supply Chain Attacks
To mitigate the risk of vendor attacks, organizations should implement the following measures:
Vendor Risk Management:
- Conduct thorough due diligence on vendors, including assessing their security practices.
- Require vendors to adhere to strict security standards and certifications.
- Regularly monitor vendor performance and security posture.
Software Supply Chain Security:
- Use trusted software sources and avoid downloading software from unverified websites.
- Keep software and operating systems up-to-date with the latest security patches.
- Implement secure software development practices to minimize vulnerabilities.
Employee Awareness and Training:
- Educate employees about the risks of vendor attacks and phishing scams.
- Train employees to identify and report suspicious emails and websites.
- Conduct regular security awareness training to reinforce good security practices.
Network Security:
- Implement strong network security measures, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and intrusion prevention systems.
- Segment networks to limit the impact of a potential breach.
- Monitor network traffic for signs of malicious activity.
Incident Response Planning:
- Develop a comprehensive incident response plan to respond effectively to security breaches.
- Test the incident response plan regularly to ensure its effectiveness.
By adopting a proactive approach to third party security, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to these devastating attacks.
